Air purifiers, sometimes called air cleaners, help clean the air in our homes by removing dust, dander, pollen, odors, and other irritants. Air purifiers use several different technologies to tackle indoor air pollution. While most of these technologies work, some might harm your health.
In this post, I’ll cover the different popular air purifiers so you can make an informed decision while shopping for one. Enjoy.
1. HEPA Air Purifiers
HEPA, short for High-Efficiency Particulate Air, is one of the most common types of air purification technology. HEPA filters trace their origin back to WWII when they were developed to clean up dangerous chemicals and radioactive particles. HEPA filtrations are very useful in workplaces, homes, and factories where dust is a byproduct of the manufacturing process.
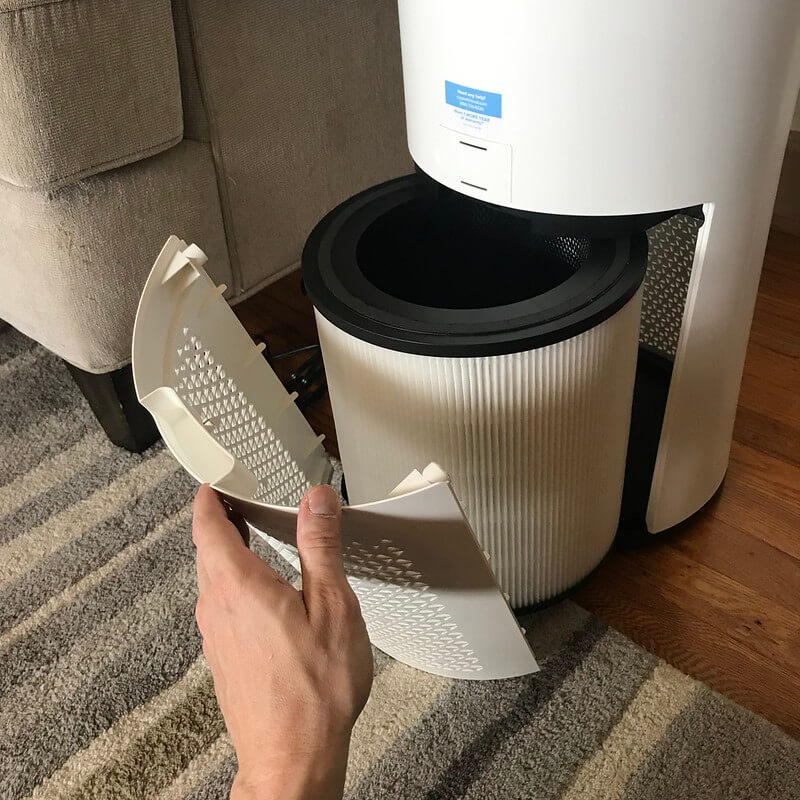

HEPA filters can be made of borosilicate glass fibers, plastic fibers like polypropylene, or fiberglass fibers.
According to NIOSH, for an Air filter to be classified as a HEPA filter, it has to trap 99.97% of dust particles that are 0.3 microns in diameter. To put this into perspective, a typical human air size is about 50 microns. So, 0.3 microns are several over 100 times smaller. So, how does this type of filter work?
How do HEPA Air Purifiers Work?
First, contaminated air is drawn into the air purifier using a fan. Then the fan forces the air through a filter where contaminants and other particles get trapped in several ways. The bigger particles get trapped by direct impact and strain. This is when the particles are large enough to get through the filter.
Particles that are smaller than 1 micron, like, bacteria, will still pass through the filter. However, because they are a bit heavy, some of them will get trapped as they follow air through the air filter fiber. This is referred to as interception.
Smaller particles that could easily pass through a HEPA filter to their freedom get trapped by a process called Brownian motion. As these particles move, they collide with air molecules and move in random patterns, which causes them to stick to the fibers of the air filter.
Application of HEPA Air Purifiers
Generally, HEPA air purifiers are used in homes to control the spread of particulate matter and both toxic and infectious agents in the air. HEPA air purifiers are best if you or a family member suffers from allergies or asthma. This is because the filter can capture mold spores, pollen, fine dust, pet dander, bacteria, and allergens.
2. Activated Carbon Air Purifiers
Activated carbon is just the normal carbon that has been processed to make it very porous, thus giving it a larger surface area for adsorption.
Rather than absorbing particles, activated carbon air purifiers adsorb some gases and odor-causing molecules from the air. Activated carbon air purifiers can also be improved to filter out more different airborne chemicals through a process called chemical doping.
Despite their numerous benefits, activated carbon air purifiers rarely use a standalone carbon filter because they are not as effective against particulates. Many air purifiers that use activated carbon comes with HEPA air filters.
How do Activated Carbon Air Purifiers work?
Activated carbon air purifiers remove air pollutants through a process known as adsorption, which is different from absorption. In absorption, the substance being removed is absorbed into the structure of the absorbent. This is how a sponge absorbs water. However, in adsorption, the substances (pollutants) stick outside the carbon.
As the air gets into the air purifier and is forced via the activated carbon filters, the carbon adsorbs air pollutants, trapping them. According to a paper by the Ohio Environmental Agency (2), a single gram of activated carbon can have hundreds of square meters in surface area for adsorption.
Application of Activated Carbon Air Purifiers
Air purifiers with activated carbon are especially helpful for people suffering from Multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS). This is a condition attributed to exposure to low levels of known gaseous chemicals such as formaldehyde found in carpets, perfumes, and other chemicals in household cleaning products. Carbon air filters can also remove volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) that other types of air purifiers cannot effectively filter. Some gases given off by smoking cigarettes or drying paint can also be removed.
Apart from chemicals, activated carbon air purifiers can also remove unpleasant odors created by various gaseous chemicals, though not all of them.
3. Ionic Air Purifiers
Ionic air purifiers, air ionizers, or ion generators are a type of air purifier technology that grew popular in the 1990s and early 2000s. Part of the reasons they became a choice for many people is because they are quiet, energy-efficient, and, best of all, do not require regularly replacing filters, which is economical.
Ionic air purifiers come in different forms. Some fanless models rely on air currents to carry the particles, while others use a fan to speed up things. Ionic air purifiers can be standalone or combined with other air purification technologies to improve their effectiveness.
How do Ionic Air Purifiers work?
Unlike other types of air purifiers, Ionic air purifiers do not use a filter. Instead, ionizers create negatively charged ions through a process known as corona discharge. As the negative ions get released by the air purifier, they bond with positively charged air pollutants and settle inside the air purifier or on the surfaces around your home.
There are two ionic air purifiers: ion generators and electrostatic precipitators.
Ion generators release negatively charged ions into the air for purification. The negative ions bind to charge pollutants and positively fall onto your home surfaces.
Electrostatic precipitators still employ the same idea as ion generators. However, instead of the negative ions being released into the air and settling on outside surfaces, the air purifier first pulls air using a fan. As the air passes through the air purifier, it goes through negatively and positively charged plates. The air pollutants are attracted to the plates where they can be washed off.
For this reason, electrostatic precipitators are more popular than ionizing air purifiers because you can easily clean the plates compared to the whole room.
Application of Ionic Air Purifiers
Ionic air purifiers can only remove particulate pollutants in the air. This includes the likes of dust, mold spores, pollen, or pet dander. Compared to other models that use HEPA filters to eliminate particulate matter, it is better to use a HEPA air purifier for better efficiency.
Ionizers do not remove gaseous pollutants, odors, or VOCs from the air. On the flipside, ionic air purifiers release Ozone gas as a byproduct, which can harm your lungs. Ozone also reacts with other household pollutants to form gases like formaldehyde.
If you choose an ionic air purifier, go with electrostatic precipitators. Ensure you clean the plates regularly and the area around the air purifier, preferably with a vacuum cleaner.
4. Ozone Air Purifiers
Ozone is a very reactive gas that is composed of three oxygen atoms. Ozone can be artificial or naturally occurring in the Earth’s upper atmosphere. Ozone in air purifiers effectively eliminates strong odors and other airborne chemicals. Similar to air fresheners, Ozone has a very fresh scent to it. The fresh scent bundled together with the ability to remove odors makes Ozone air purifiers appealing to consumers.
However, health concerns have arisen from using Ozone as an air purifying technology. According to EPA, “NO agency of the federal government has approved these devices for use in occupied spaces”.Ozone, when exhaled, can damage the lungs and cause chest pains, coughing, throat irritation, and shortness of breath.
EPA has also noted that some Ozone air purifiers manufacturers or vendors use deceptive terms like “energized oxygen” or “pure air,” which suggest a healthier kind of oxygen when things are not that way.
The state of California has banned the use of ozone air purifiers due to studies that found these machines can worsen health conditions such as asthma, which manufacturers and marketers claim they help prevent.
How does Ozone Air Purifiers work?
Ozone air purifiers, as we’ve seen, work by producing Ozone. These machines can generate Ozone either by corona discharge or ultraviolet radiation. Both of these methods split 02 to form individual oxygen atoms.
Once split, individual oxygen atoms recombine into three oxygen atoms, called Ozone. The Ozone is released by pumping it into the home’s air for purification. Though it helps remove odors and kill microbes, Ozone does not remove particulate matter in the air. Most ozone air purifiers will come with an ionizer to help remove particulate matter.
Application of Ozone Air Purifiers
A cozy indoor, we do not recommend using ozone air purifiers in a home setting. This is because there have been studies showing their dangers to human health, and there are no approved ozone generators for homes by the US government.
However, Ozonators have been used in industrial applications for decontamination, odor treatment, and eliminating pathogens, bacteria, and other microorganisms in the air, surfaces, and water.
5. UV Light Air Purifiers
Ultraviolet light is a type of electromagnetic radiation produced in nature by the sun. UV light works by altering the DNA or RNA of microbes rendering them harmless. There are different forms of UV light, including UV-A (Blacklight), UV-B, and UV-C. UV-C is the form of UV light that is used for purification purposes.
Historically, UV light has been used to disinfect water and other surfaces. Ultraviolet light C or UV-C is also used in hospitals to cut the transmission of bacteria and other microbes that linger in patients’ rooms. UV-C is also referred to as Germicidal UV light.
UV light can also be used in air purifiers to inactivate airborne microbes. This technology in air purifiers is referred to as UV germicidal irradiation or UVGI air purifiers.
How do UV Light Air Purifiers work?
Like most air purifiers, UV light purifiers first begin by sucking the air into the machine using a fan.
Inside the air purifier are UV lamps, which give off UV-C light. Depending on the material used for emitting the light, e.g., phosphor or quartz, the light may not be visible or blueish. Most household air purifiers use short-wave low-pressure mercury lamps to clean the air.
As air passes through the air purifier, bulbs emit UV-C shine, thus killing microbes and other pathogens. Usually, UV light air purifiers combine with another filter like HEPA filters.
Factors such as the type of ultraviolet lamp used, temperature, and humidity will affect the performance.
Application of UV Light Air Purifiers
UV air purifiers can be used to target airborne microbes and other microorganisms. They have a wide range of applications for antiviral and antibacterial purification. Most UV light air purifiers are advertised to reduce mold allergens and dust mites. The effectiveness of UV air purifiers has long been debated. The technology has also come under fire due to the production of Ozone as a byproduct of the process.
Choose the Right Air Purifier
Each technology used in air purifiers can improve indoor air quality depending on the pollutant. Before making up your mind, first, consider the type of air pollutant found in your home.
Two types of indoor air pollutants affect air quality. They can be categorized under particulate and gaseous pollutants. Particulate matter includes dust, pollen, animal dander, particles generated from combustion appliances, and particles associated with tiny living organisms such as molds, dust mites, and bacteria. Gaseous pollutants come from combustion processes and building materials or furnishings that use adhesives, varnishes, and cleaning products.
There are also other new air cleaning technologies such as photocatalytic and probiotics air purifiers that we did not include in this list. Apart from the type of air purifier, the size of your room, the location of the air purifier, maintenance, and features included should also be factored in a while making your final decision.

